| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
- 이메일 전송
- 카카오로그인
- logstash
- JavaScript
- TypeScript
- react-slick
- 위크맵
- context switch
- DB
- Mongoose
- AGGREGATE
- nest
- 객체
- nodemailer
- 참조에 의한 객체 복사
- javacript
- 화살표 함수
- nestjs
- MongoDB
- JSON.stringify
- 구조 분해 할당
- 카카오 소셜로그인
- 자바스크립트
- 캐러셀
- 로그스태시
- Map
- JSON.parse
- 위크셋
- 중첩 구조 분해
- nextjs
- Today
- Total
뚜sh뚜sh
Memory Management3 본문
Multilevel Paging and Performance
- Address space가 더 커지면 다단계 페이지 테이블 필요
- 각 단계의 페이지 테이블이 메모리에 존재하므로 logical address의 physical address 변환에 더 많은 메모리 접근 필요
- TLB를 통해 메모리 접근 시간을 줄일 수 있음
- 4단계 페이지 테이블을 사용하는 경우

Valid(v) / Invalid(i) Bit in a Page Table

Memory Protection
- Page table의 각 entry 마다 아래의 bit를 둔다
1. Protection bit
- page에 대한 접근 권한(read/write/read-only)
2. Valid-invalid bit
- "valid"는 해당 주소의 frame에 그 프로세스를 구성하는 유효한 내용이 있음을 뜻함(접근 허용)
- "invalid"는 해당 주소의 frame에 유효한 내용이 없음*을 뜻함(접근 불허)
* i) 프로세스가 그 주소 부분을 사용하지 않는 경우
ii) 해당 페이지가 메모리에 올라와 있지 않고 swap area에 있는 경우
Inverted Page Table
- page table이 매우 큰 이유
- 모든 process 별로 그 logical address에 대응하는 모든 page에 대해 page table entry가 존재
- 대응하는 page가 메모리에 있는 아니든 간에 page table에는 entry로 존재
- Inverted page table
- Page frame 하나당 page table에 하나의 entry를 둔 것(system-wide)
- 각 page table entry는 각각의 물리적 메모리의 page frame이 담고 있는 내용 표시(process-id, process의 logical address)
- 단점 : 테이블 전체를 탐색해야 함
- 조치 : associative register 사용(expensive)
Inverted Page Table Architecture

Shared Page
- Shared code
- Re-entrant Code(=Pure code)
- read-only로 하여 프로세스 간에 하나의 code만 메모리에 올림(eg, text editors, compilers, window systems)
- Shared code는 모든 프로세스의 logical address space에서 동일한 위치에 있어야 함
- Private code and data
- 각 프로세스들은 독자적으로 메모리에 올림
- Private data는 logical address space의 아무 곳에 와도 무방
Shared Pages Example

Segmentation
- 프로그램은 의미 단위인 여러 개의 segment로 구성
- 작게는 프로그램을 구성하는 함수 하나하나를 세그먼트로 정의
- 크게는 프로그램 전체를 하나의 세그먼트로 정의 가능
- 일반적으로는 code, data, stack 부분이 하나씩의 세그먼트로 정의됨
- Segment는 다음과 같은 logical unit들임
- main()
- function
- global variables
- stack
- symbol table
- arrays
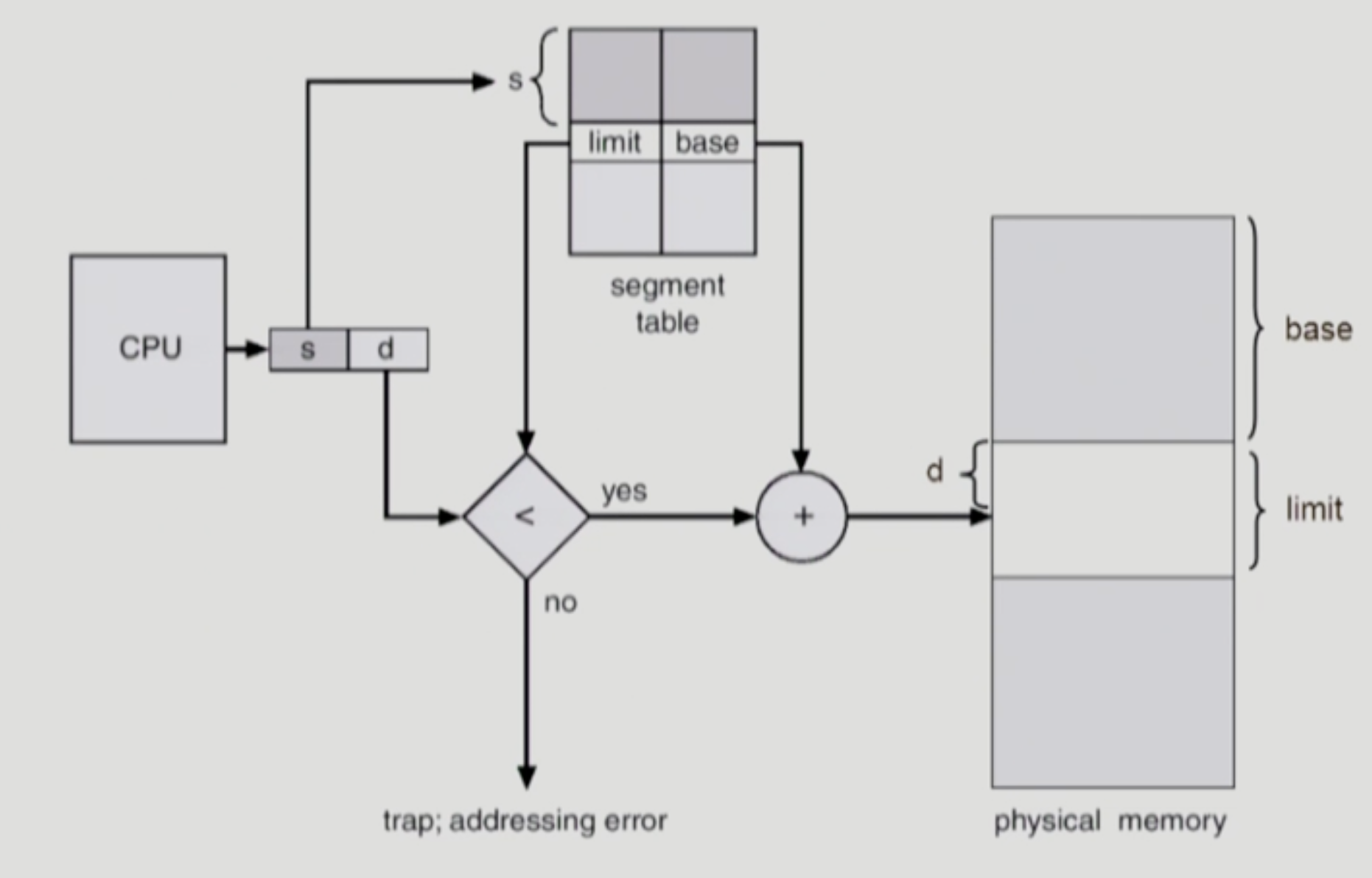
Segmentation Architecture
- Logical address는 다음의 두 가지로 구성
- <segment-number, offset>
- Segment table
each table entry has:
- base-starting physical address of the segment
- limit-length of the segment
- Segment-table base register(STBR)
- 물리적 메모리에서의 segment table의 위치
- Segment-table length register(STLR)
- 프로그램이 사용하는 segment의 수
- segment number s is legal if s < STLR
Segmentation Hardware
Segmentation Architecture(Cont.)
- Protection
1. 각 세그먼트 별로 protection bit가 있음
2. Each entry:
- Valid bit = 0 => illegal segment
- Read/Write/Execution 권한 bit
- Sharing
- shared segment
- same segment number
※ segment는 의미 단위이기 때문에 공유(sharing)와 보안(protection)에 있어 paging보다 훨씬 효과적이다
- Allocation
- first fit / best fit
- external fragmentation 발생
※ segment의 길이가 동일하지 않으므로 가변분할 방식에서와 동일한 문제점들이 발생
'운영체제' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Virtual Memory1 (0) | 2023.07.17 |
|---|---|
| Memory Management4 (0) | 2023.07.14 |
| Memory Management2 (0) | 2023.07.11 |
| Memory Management1 (0) | 2023.07.10 |
| Deadlock2 (0) | 2023.07.10 |




